
LPG is one of the most commonly used fuels in India. It is present in almost every household kitchen, as a reliable source of energy for daily cooking. At the same time, LPG is also used as an alternative automotive fuel, powering thousands of vehicles across cities and highways. As the same term “LPG” is used in both domestic and automotive contexts, many people naturally assume that cooking LPG and auto LPG are the same fuel, simply applied in different ways.
This assumption is incorrect.
While both fuels belong to the LPG category, cooking LPG and auto LPG are developed for completely different operating conditions. The environment inside a kitchen and the environment inside a moving vehicle are not comparable. As a result, the two fuels differ in their chemical composition, pressure handling, storage design, safety mechanisms, and regulatory standards. These differences are intentional and essential for safe and efficient use.
Using cooking LPG in a vehicle or using auto LPG for cooking is not just a matter of improper application. It can lead to serious safety risks, damage to equipment, violation of fuel regulations, and legal consequences. Each type of LPG is engineered to perform reliably only within its intended system.
This blog explains the difference between cooking LPG and autogas (auto LPG) and why they must always be used only for their specific applications.
LPG stands for Liquefied Petroleum Gas. It is produced during crude oil refining and natural gas processing. Under moderate pressure, LPG turns into a liquid, which makes it easy to store and transport. When released, it converts back into gas and burns efficiently.
LPG is widely used in India because it offers high energy output, clean combustion, and dependable performance across different weather conditions. Compared to petrol and diesel, it produces fewer harmful emissions and is easier to handle when stored in a proper way.
However, liquefied petroleum gas is not supplied in a single standard form. The proportion of gases, operating pressure, and safety systems vary depending on where and how the fuel is used. This is where the difference between cooking LPG and auto LPG becomes important.
Using clean fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) for cooking offers clear advantages over traditional biomass fuels commonly used in India. LPG provides a bright flame, reduces smoke inside kitchens, and supports healthier cooking environments for families.
Today, cooking LPG is widely used in urban homes, restaurants, hotels, and commercial kitchens, and its adoption is steadily growing in rural areas as well.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has assigned IS 4576 as the official standard for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) used for cooking purposes in India.
Cooking LPG generally contains a higher proportion of butane and a lower proportion of propane. It’s because butane burns smoothly at lower pressure, which makes it suitable for cooking appliances.
This composition helps achieve:
Cooking LPG is stored inside cylinders at moderate pressure. Before reaching the stove, the gas passes through a regulator that reduces the pressure to a very low and safe level.
Low pressure is essential because:
Liquefied petroleum gas used in cooking contains a strong odorant that helps detect leaks easily. The cylinders are kept in a fixed place (may be in a cabinet below the stove) and are not moved frequently.
But how can you check if your cooking LPG is safe?
Auto LPG is an automotive-grade LPG used in vehicles, such as LPG cars, buses, trucks, etc. It has a specially engineered fuel system that is capable of handling higher pressure, constant vehicle movement, and changes in engine load during driving.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has assigned IS 14861 as the official standard for auto LPG used in automotive applications in India.
Autogas contains a higher proportion of propane compared to cooking LPG. Propane vaporises more easily and performs reliably over a wide temperature range.
This composition ensures:
Auto LPG is stored at much higher pressure than cooking LPG. This allows the fuel to remain in liquid form inside the vehicle tank until it reaches the engine vaporiser.
Higher pressure is necessary because:
Note: Low-pressure LPG systems used in kitchens cannot meet these requirements.
In LPG cars, auto LPG is stored in special fuel tanks made only for vehicles. These tanks are much stronger than household LPG gas cylinders and are built to hold gas safely at high pressure while the car is running.
LPG tanks used in cars have safety parts, such as:
Read More: Why Consumers Are Shifting from Petrol and Diesel to Autogas
Now that you know what cooking LPG and auto LPG are used for, given below is a comparison to help you understand how they are different in every aspect.
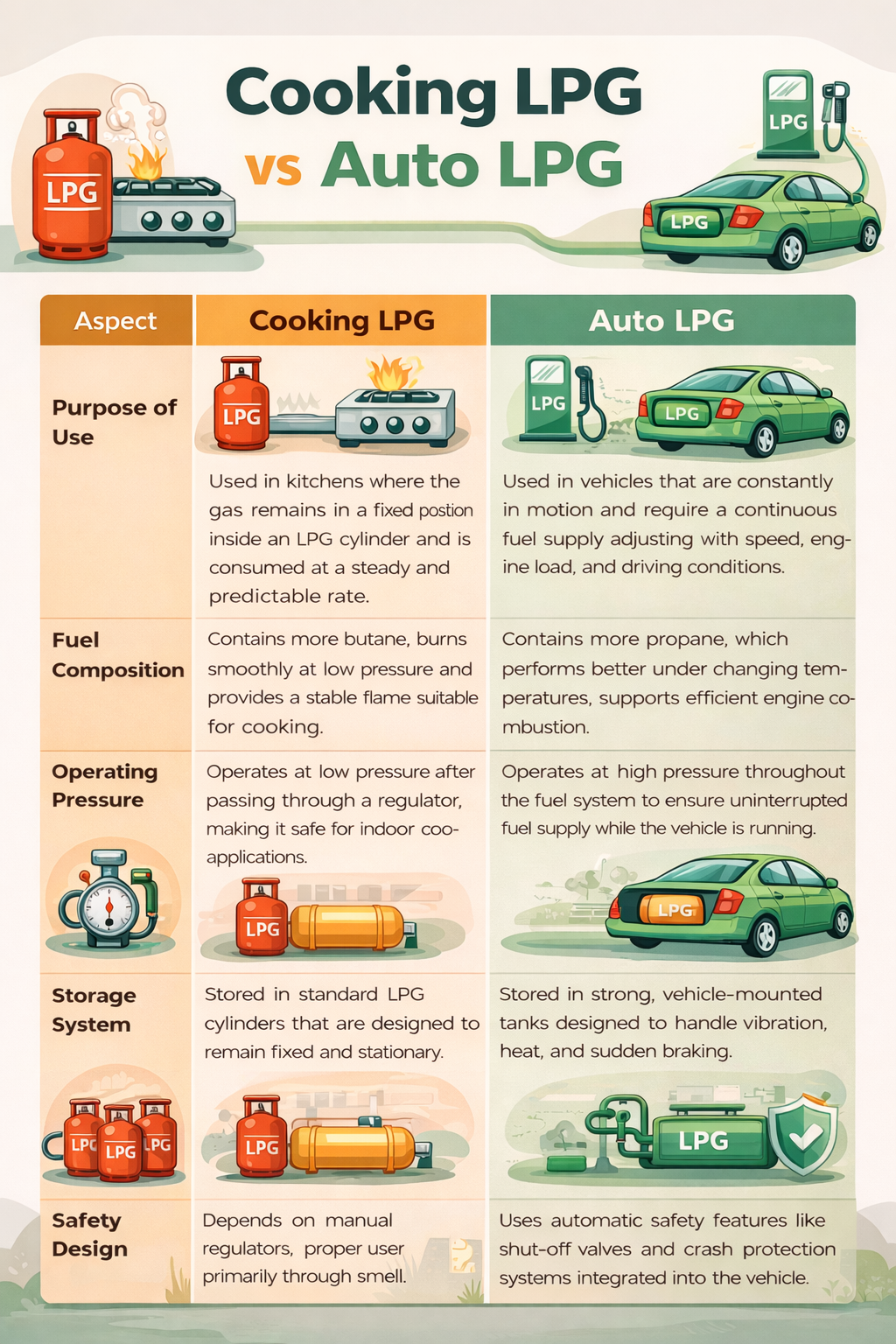
Cooking LPG and auto LPG are both liquefied petroleum gas. But their composition, storage system, operating pressure and safety procedures are different. Problems arise only when this distinction is ignored. Treating both fuels as interchangeable can lead to safety risks, equipment damage, and regulatory issues. Understanding this difference helps consumers avoid unsafe practices and make informed decisions based on facts rather than assumptions.
Ans. Yes, AutoGas is a type of LPG. It is LPG that has been specially processed and supplied for use in vehicles. While it comes from the same LPG family, AutoGas is meant for automotive engines and follows different safety and performance standards than cooking LPG.
Ans. Yes, LPG can be used in a vehicle only if the vehicle is LPG-compatible and uses auto LPG (AutoGas). Cooking LPG from an LPG gas cylinder should never be used in a vehicle. LPG cars require a dedicated fuel system and must be refuelled only at authorised AutoGas stations.
Ans. No, LP gas and LPG generally refer to the same fuel. LP gas is simply a shortened form of Liquefied Petroleum Gas. In everyday use, both terms are used interchangeably, though LPG is the more commonly used term in India.
Ans. On average, an LPG car gives around 22 to 26 kilometres per kilogram, depending on the vehicle type, engine condition, driving style, and traffic conditions.
Comment (0)